Abstract
Task and Motion Planning (TAMP) has made strides in complex manipulation tasks, yet the execution robustness of the planned solutions remains overlooked. In this work, we
propose a method for reactive TAMP to cope with runtime uncertainties and disturbances. We combine an Active Inference planner (AIP) for adaptive high-level action selection and a
novel Multi-Modal Model Predictive Path Integral controller (M3P2I) for low-level control. This results in a scheme that simultaneously adapts both high-level actions and low-level motions.
The AIP generates alternative symbolic plans, each linked to a cost function for M3P2I. The latter employs a physics simulator for diverse trajectory rollouts, deriving optimal control
by weighing the different samples according to their cost. This idea enables blending different robot skills for fluid and reactive plan execution, accommodating plan adjustments at both the
high and low levels to cope, for instance, with dynamic obstacles or disturbances that invalidate the current plan. We have tested our approach in simulations and real-world scenarios.
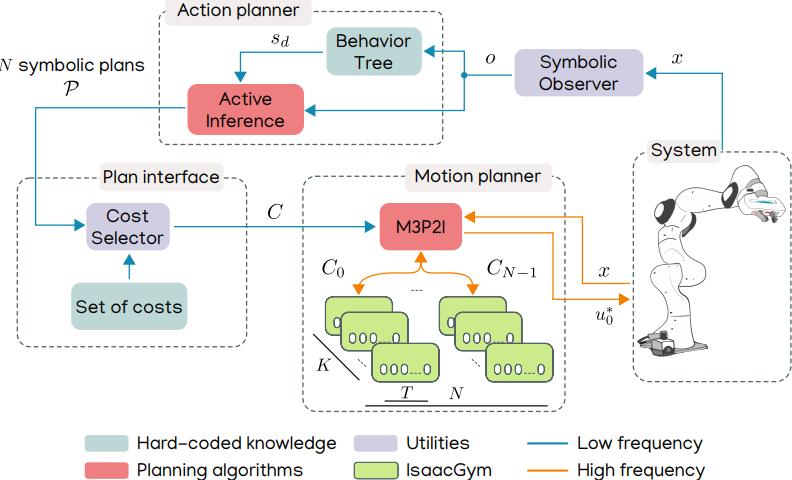
Proposed Scheme
Given symbolic observations $o$ of the environment, the action planner computes $N$ different plan alternatives linked to individual cost functions $C_i$. M3P2I samples control input sequences and uses an importance sampling scheme to approximate the optimal control $u_0^*$.
Simulation Results
Push only using MPPI
Middle to corner -- success
Push only using MPPI
Corner to corner -- fail
Pull only using MPPI
Middle to corner -- fail
Pull only using MPPI
Corner to corner -- fail
Multi-modal motion using M3P2I
Middle to corner -- success
Multi-modal motion using M3P2I
Corner to corner -- success
Reactive pick using MPPI
Pick from top
Multi-modal pick using M3P2I
Top pick and side pick
Multi-modal motion using M3P2I
With collision avoidance
Reactive pick using RL
Oscillation occurs when introducing disturbance
Dynamic Risk-Aware MPPI for Mobile Robots in Crowds via Efficient Monte Carlo Approximations
Elia Trevisan,
Khaled A. Mustafa,
Godert Notten,
Xinwei Wang,
Javier Alonso-Mora.
In IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS),
2025.
Deploying mobile robots safely among humans requires the motion planner to account for the uncertainty in the other agents' predicted trajectories. This remains challenging in traditional approaches, especially with arbitrarily shaped predictions and real-time constraints. To address these challenges, we propose a Dynamic Risk-Aware Model Predictive Path Integral control (DRA-MPPI), a motion planner that incorporates uncertain future motions modelled with potentially non-Gaussian stochastic predictions. By leveraging MPPI's gradient-free nature, we propose a method that efficiently approximates the joint Collision Probability (CP) among multiple dynamic obstacles for several hundred sampled trajectories in real-time via a Monte Carlo (MC) approach. This enables the rejection of samples exceeding a predefined CP threshold or the integration of CP as a weighted objective within the navigation cost function. Consequently, DRA-MPPI mitigates the freezing robot problem while enhancing safety. Real-world and simulated experiments with multiple dynamic obstacles demonstrate DRA-MPPI's superior performance compared to state-of-the-art approaches, including Scenario-based Model Predictive Control (S-MPC), Frenét planner, and vanilla MPPI.
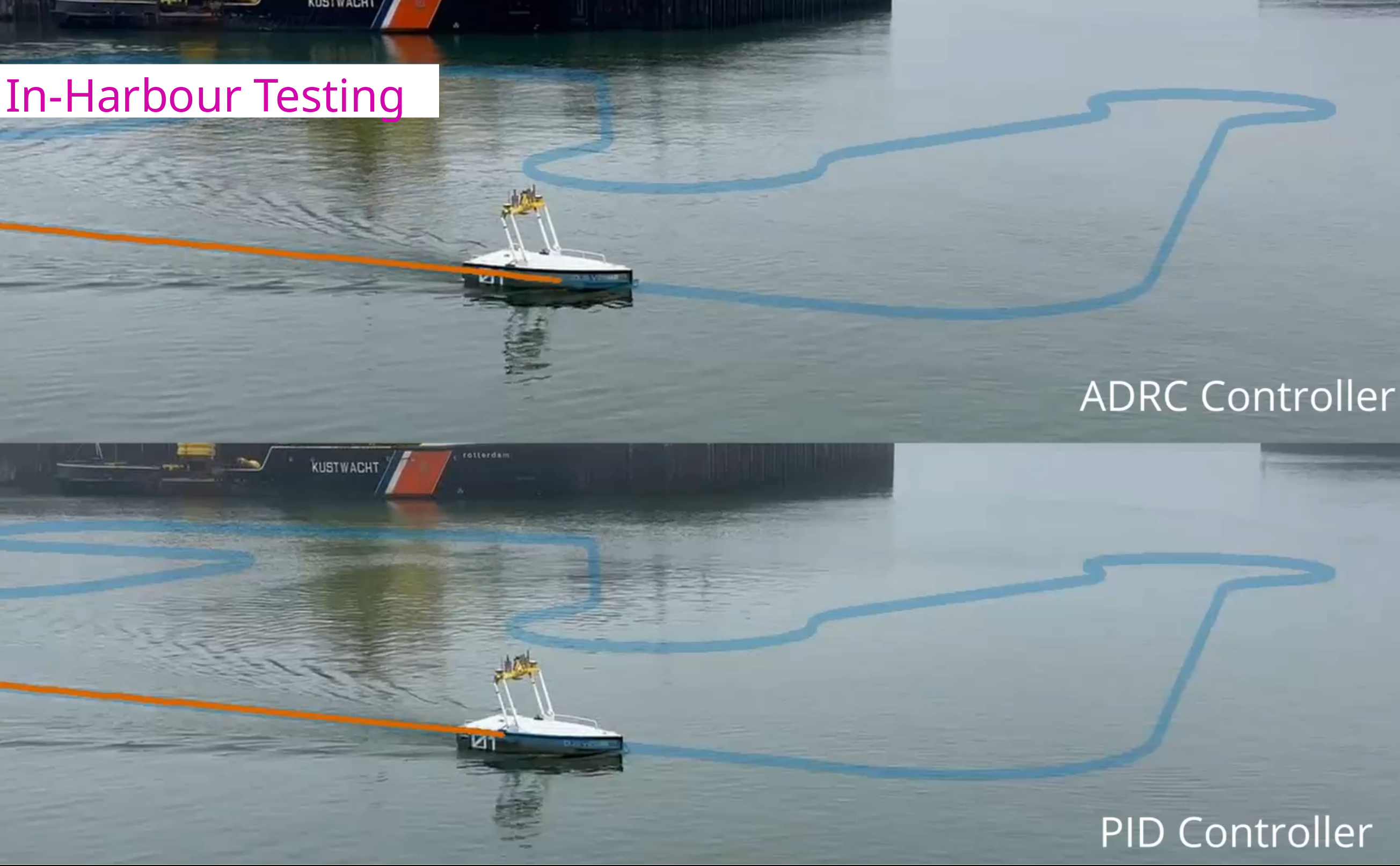
Active Disturbance Rejection Control (ADRC) for Trajectory Tracking of a Seagoing USV: Design, Simulation, and Field Experiments
Jelmer van der Saag,
Elia Trevisan,
Wouter Falkena,
Javier Alonso-Mora.
In IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS),
2025.
Unmanned Surface Vessels (USVs) face significant control challenges due to uncertain environmental disturbances like waves and currents. This paper proposes a trajectory tracking controller based on Active Disturbance Rejection Control (ADRC) implemented on the DUS V2500. A custom simulation incorporating realistic waves and current disturbances is developed to validate the controller's performance, supported by further validation through field tests in the harbour of Scheveningen, the Netherlands, and at sea. Simulation results demonstrate that ADRC significantly reduces cross-track error across all tested conditions compared to a baseline PID controller but increases control effort and energy consumption. Field trials confirm these findings while revealing a further increase in energy consumption during sea trials compared to the baseline.

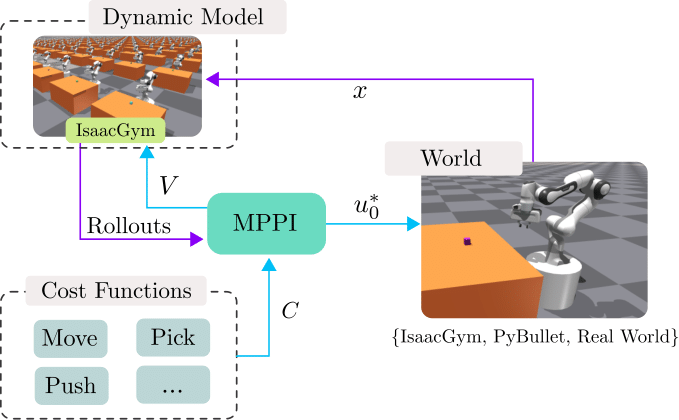
Sampling-based Model Predictive Control Leveraging Parallelizable Physics Simulations
Corrado Pezzato,
Chadi Salmi,
Elia Trevisan,
Max Spahn,
Javier Alonso-Mora,
Carlos Hernández Corbato.
In IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L),
2025.
We present a method for sampling-based model predictive control that makes use of a generic physics simulator as the dynamical model. In particular, we propose a Model Predictive Path Integral controller (MPPI), that uses the GPU-parallelizable IsaacGym simulator to compute the forward dynamics of a problem. By doing so, we eliminate the need for manual encoding of robot dynamics and interactions among objects and allow one to effortlessly solve complex navigation and contact-rich tasks. Since no explicit dynamic modeling is required, the method is easily extendable to different objects and robots. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this method in several simulated and real-world settings, among which mobile navigation with collision avoidance, non-prehensile manipulation, and whole-body control for high-dimensional configuration spaces. This method is a powerful and accessible tool to solve a large variety of contact-rich motion planning tasks.
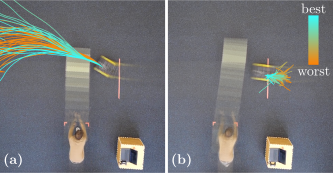
Biased-MPPI: Informing Sampling-Based Model Predictive Control by Fusing Ancillary Controllers
Elia Trevisan,
Javier Alonso-Mora.
In IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L),
2024.
Motion planning for autonomous robots in dynamic environments poses numerous challenges due to uncertainties in the robot's dynamics and interaction with other agents. Sampling-based MPC approaches, such as Model Predictive Path Integral (MPPI) control, have shown promise in addressing these complex motion planning problems. However, the performance of MPPI relies heavily on the choice of sampling distribution. Existing literature often uses the previously computed input sequence as the mean of a Gaussian distribution for sampling, leading to potential failures and local minima. In this paper, we propose a novel derivation of MPPI that allows for arbitrary sampling distributions to enhance efficiency, robustness, and convergence while alleviating the problem of local minima. We present an efficient importance sampling scheme that combines classical and learning-based ancillary controllers simultaneously, resulting in more informative sampling and control fusion. Several simulated and real-world demonstrate the validity of our approach.
Interaction-Aware Sampling-Based MPC with Learned Local Goal Predictions
W. Jansma,
E. Trevisan,
A. Serra-Gomez,
J. Alonso-Mora.
In Proc. IEEE International Symposium on Multi-Robot and Multi-Agent Systems,
2023.
Motion planning for autonomous robots in tight, interaction-rich, and mixed human-robot environments is challenging. State-of-the-art methods typically separate prediction and planning, predicting other agents' trajectories first and then planning the ego agent's motion in the remaining free space. However, agents' lack of awareness of their influence on others can lead to the freezing robot problem. We build upon Interaction-Aware Model Predictive Path Integral (IA-MPPI) control and combine it with learning-based trajectory predictions, thereby relaxing its reliance on communicated short-term goals for other agents. We apply this framework to Autonomous Surface Vessels (ASVs) navigating urban canals. By generating an artificial dataset in real sections of Amsterdam's canals, adapting and training a prediction model for our domain, and proposing heuristics to extract local goals, we enable effective cooperation in planning. Our approach improves autonomous robot navigation in complex, crowded environments, with potential implications for multi-agent systems and human-robot interaction.
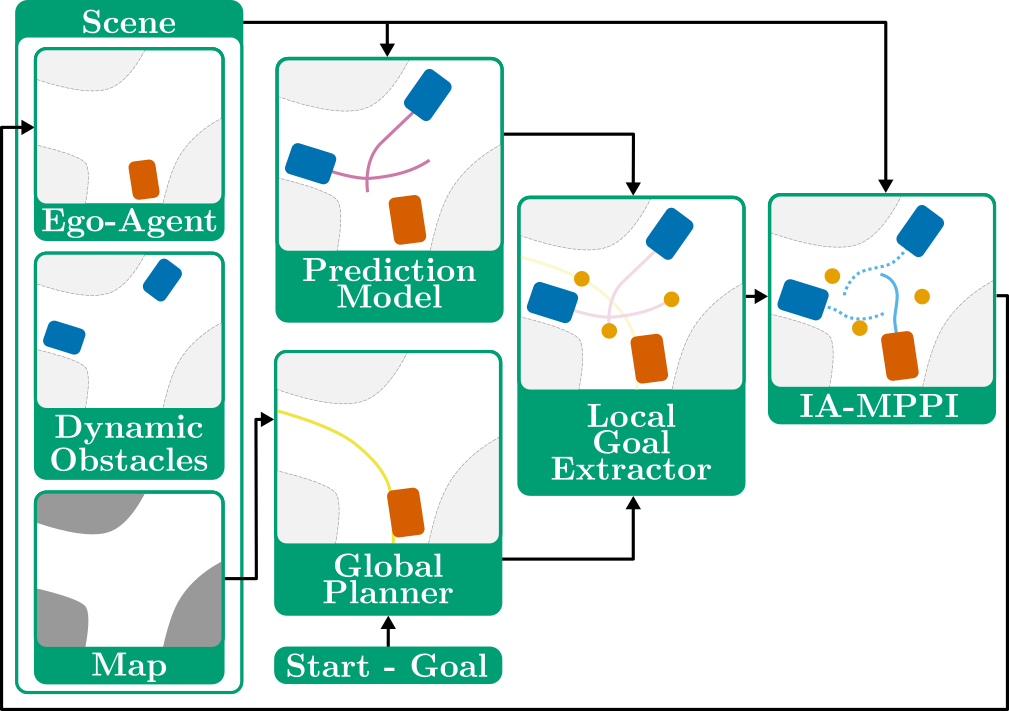
Multi-Agent Path Integral Control for Interaction-Aware Motion Planning in Urban Canals
L. Streichenberg,
E. Trevisan,
J. J. Chung,
R. Siegwart,
J. Alonso-Mora.
In , in IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA),
2023.
Autonomous vehicles that operate in urban envi- ronments shall comply with existing rules and reason about the interactions with other decision-making agents. In this paper, we introduce a decentralized and communication-free interaction-aware motion planner and apply it to Autonomous Surface Vessels (ASVs) in urban canals. We build upon a sampling-based method, namely Model Predictive Path Integral control (MPPI), and employ it to, in each time instance, compute both a collision-free trajectory for the vehicle and a prediction of other agents’ trajectories, thus modeling inter- actions. To improve the method’s efficiency in multi-agent sce- narios, we introduce a two-stage sample evaluation strategy and define an appropriate cost function to achieve rule compliance. We evaluate this decentralized approach in simulations with multiple vessels in real scenarios extracted from Amsterdam’s canals, showing superior performance than a state-of-the- art trajectory optimization framework and robustness when encountering different types of agents.
Sampling-Based MPC Using a GPU-parallelizable Physics Simulator as Dynamic Model: an Open Source Implementation with IsaacGym
C. Pezzato,
C. Salmi,
E. Trevisan,
J. Alonso-Mora,
C. Hernandez Corbato.
In Embracing Contacts Workshop at IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA),
2023.
We present a method for solving finite horizon optimal control problems using a generic physics simulator as the dynamical model. In particular, we present an open-source implementation of a model predictive path integral controller (MPPI), that uses the GPU-parallelizable IsaacGym simulator as the dynamical model to compute the forward dynamics of the system. This allows one to effortlessly solve complex contact-rich tasks such as for example, non-prehensile manipulation of a variety of objects, or picking with a mobile manipulator. Since there is no explicit dynamic modeling required from a user, the repository is easily extendable to different objects and robots, as we show in the experiments section. This makes this method a powerful and accessible tool to solve a large variety of contact-rich tasks.
Regulations Aware Motion Planning for Autonomous Surface Vessels in Urban Canals
J. de Vries,
E. Trevisan,
J. van der Toorn,
T. Das,
B. Brito,
J. Alonso-Mora.
In Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA),
2022.
In unstructured urban canals, regulation-aware interactions with other vessels are essential for collision avoidance and social compliance. In this paper, we propose a regulations aware motion planning framework for Autonomous Surface Vessels (ASVs) that accounts for dynamic and static obstacles. Our method builds upon local model predictive contouring control (LMPCC) to generate motion plans satisfying kino-dynamic and collision constraints in real-time while including regulation awareness. To incorporate regulations in the planning stage, we propose a cost function encouraging compliance with rules describing interactions with other vessels similar to COLlision avoidance REGulations at sea (COLREGs). These regulations are essential to make an ASV behave in a predictable and socially compliant manner with regard to other vessels. We compare the framework against baseline methods and show more effective regulation-compliance avoidance of moving obstacles with our motion planner. Additionally, we present experimental results in an outdoor environment.