SADCHER: Scheduling using Attention-based Dynamic Coalitions of Heterogeneous Robots in Real-Time
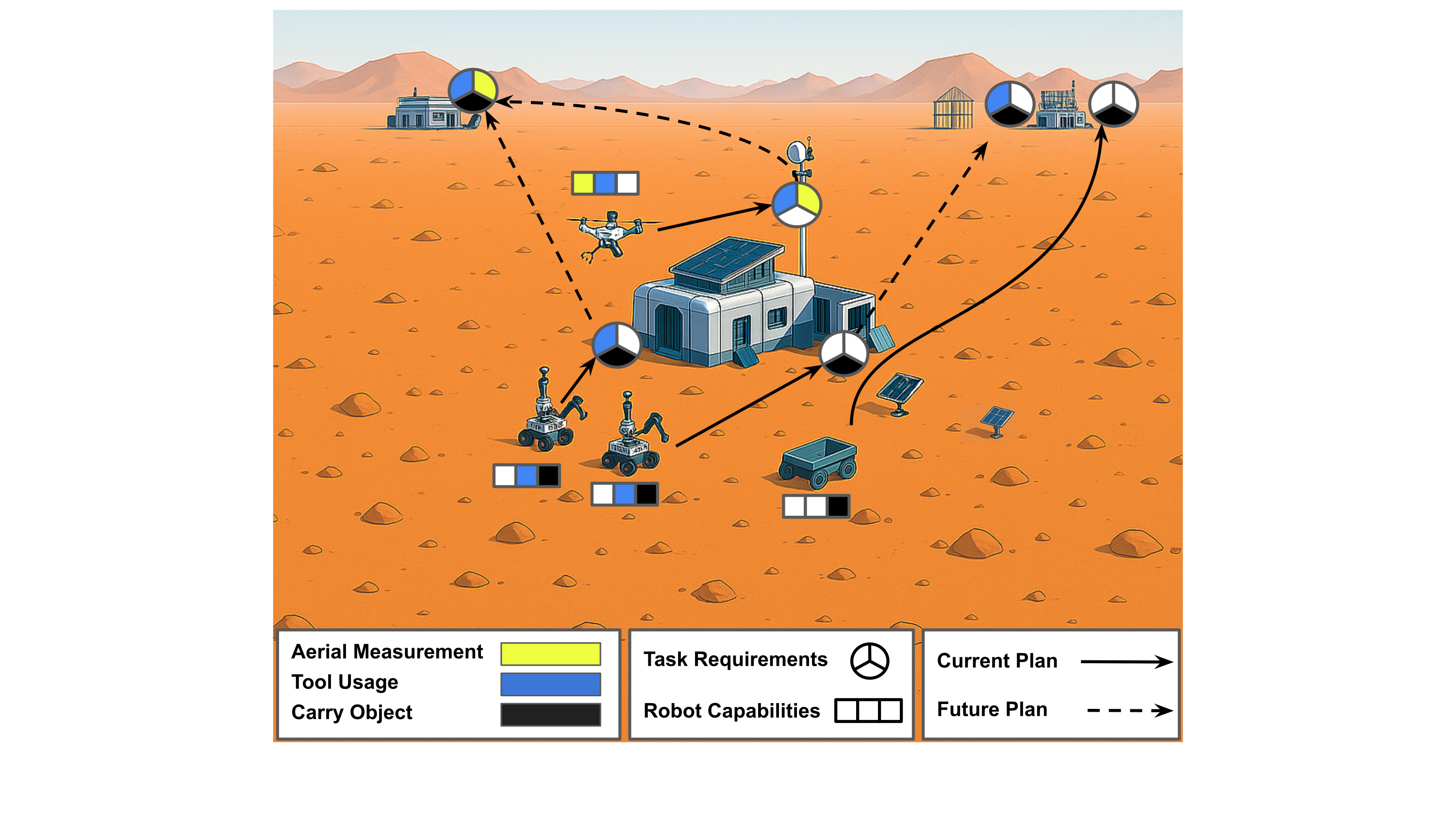
Abstract
We present Sadcher, a real-time task assignment framework for heterogeneous multi-robot teams that incorporates dynamic coalition formation and task precedence constraints. Sadcher is trained through Imitation Learning and combines graph attention and transformers to predict assignment rewards between robots and tasks. Based on the predicted rewards, a relaxed bipartite matching step generates high-quality schedules with feasibility guarantees. We explicitly model robot and task positions, task durations, and robots’ remaining processing times, enabling advanced temporal and spatial reasoning and generalization to environments with different spatiotemporal distributions compared to training. Trained on optimally solved small-scale instances, our method can scale to larger task sets and team sizes. Sadcher outperforms other learning-based and heuristic baselines on randomized, unseen problems for small and medium-sized teams with computation times suitable for real-time operation. We also explore sampling-based variants and evaluate scalability across robot and task counts. In addition, we release our dataset of 250,000 optimal schedules to facilitate future research.Method overview
The Sadcher framework consists of a neural network based on attention mechanisms to predict assignment rewards for robots to tasks that is agnostic to the size of the input graphs, i.e., can handle arbitrary numbers of robots and tasks. A re- laxed bipartite matching algorithm extracts task assignments based on the predicted reward. During runtime, the method asynchronously recomputes assignments at decision steps, i.e., when robots finish tasks or new tasks are announced. Robot and task graphs are processed by graph attention and transformer encoders and concatenated with distance features. The reward matrix is estimated by the Idle and Reward MLPs and final task assignments are extracted using relaxed bipartite matching. B: batch size, N : number of robots, M : number of tasks, d_r : robot input dimension, d_t : task input dimension, d: latent dimension.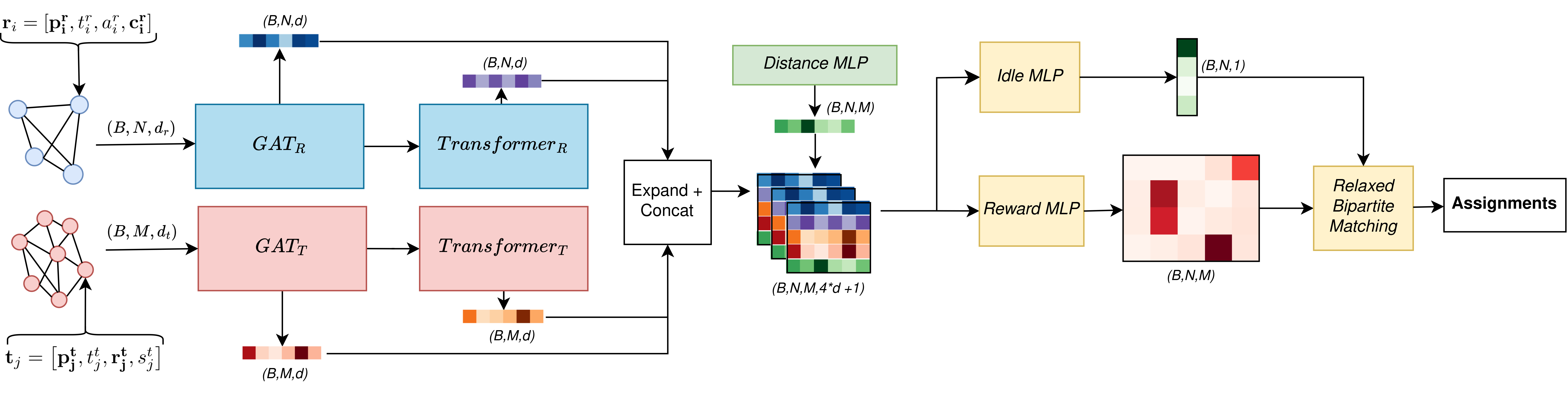
Simple Demo Video
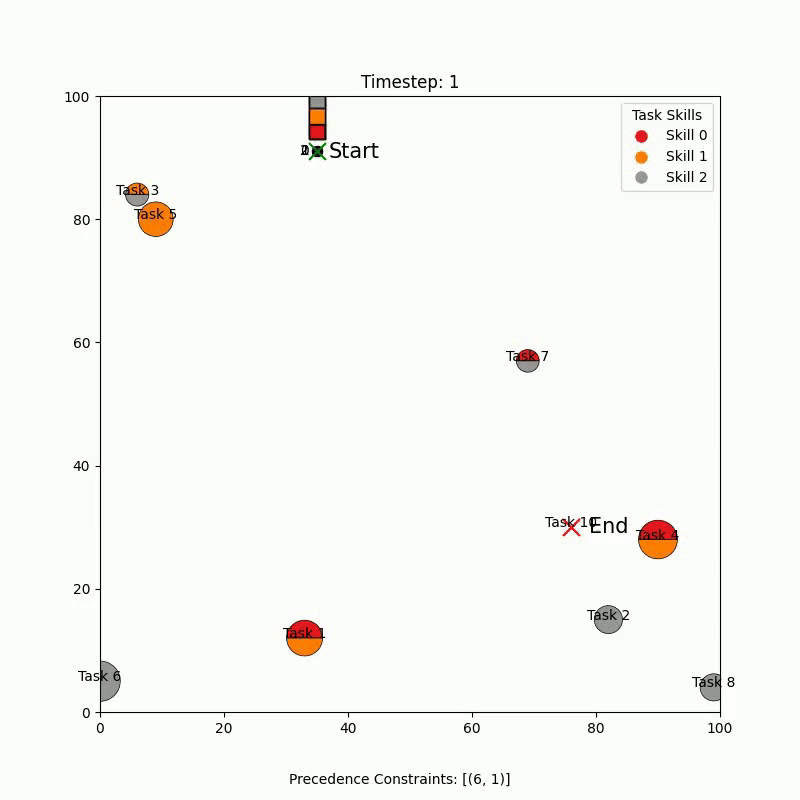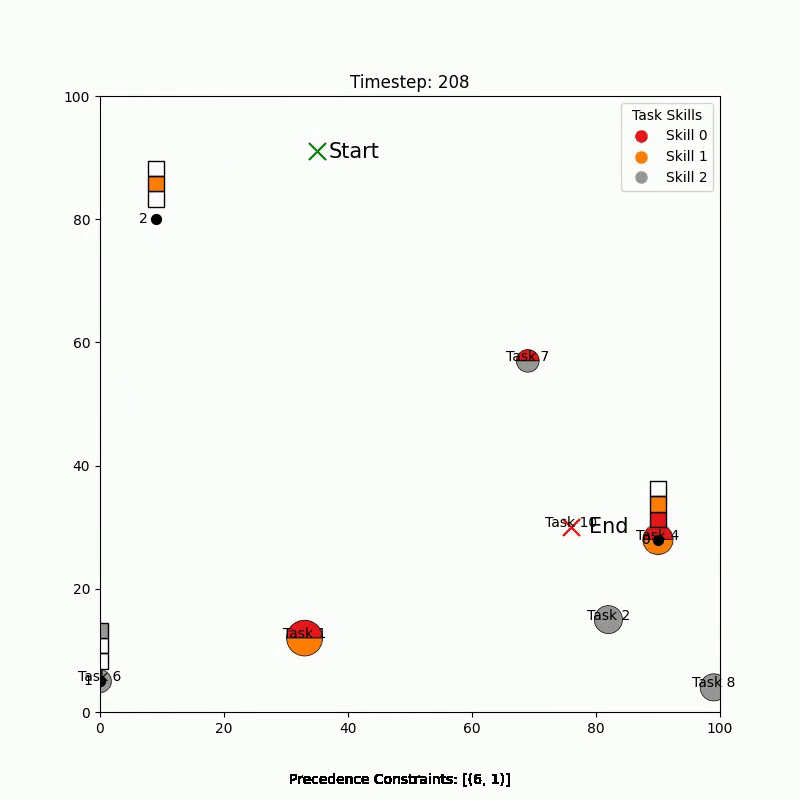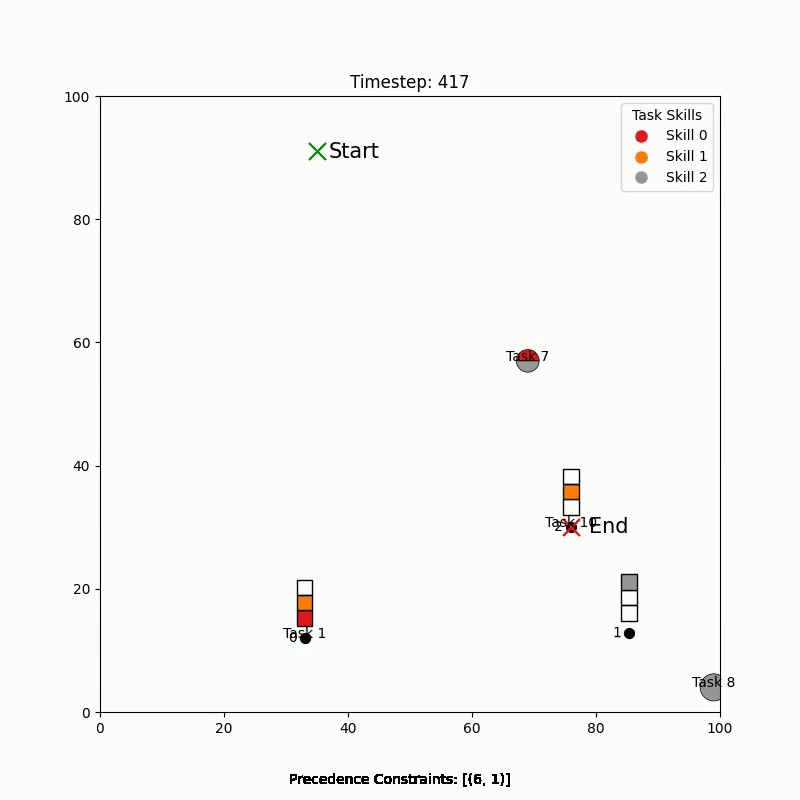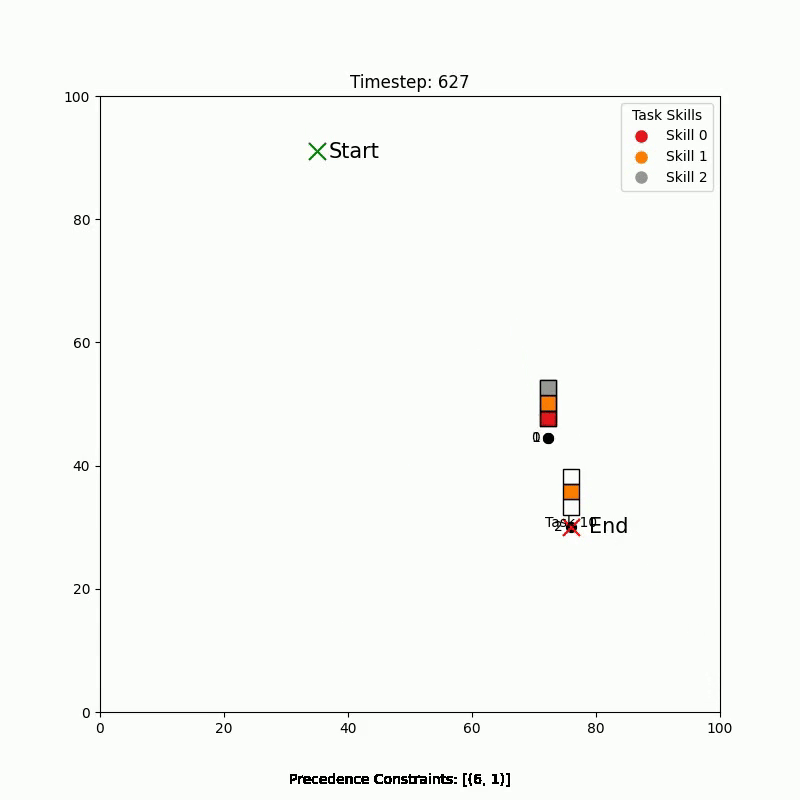
Simulation Results
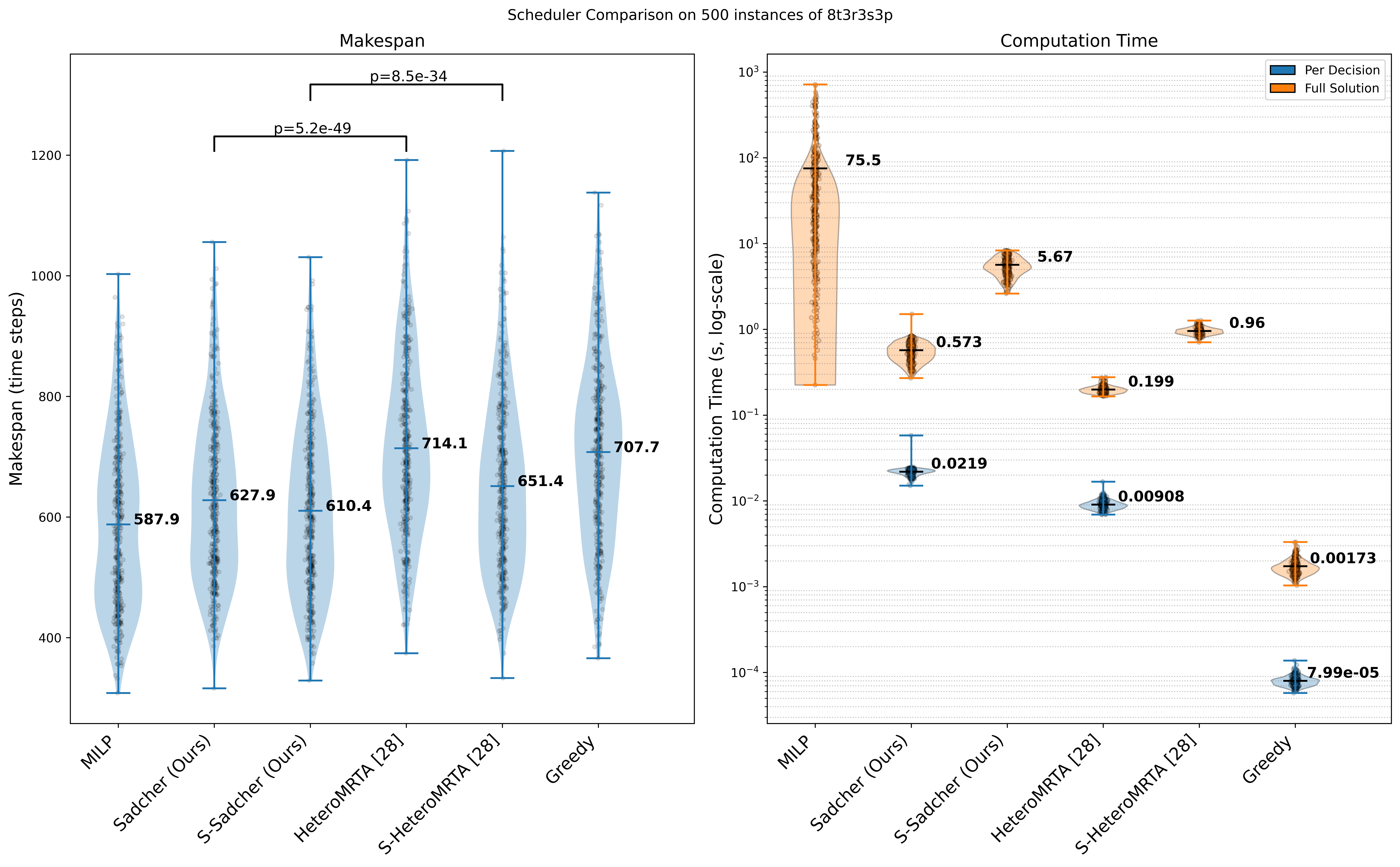
Comparison on 500 unseen, randomized problem instances (8 tasks, 3 robots, 3 precedence constraints) for makespan (left), and computation time (right). Lower means better performance. Wilcoxon significance levels are annotated for Sadcher compared to HeteroMRTA variants. All other pairwise differences are statistically significant (p < 0.05), except between S-HeteroMRTA and Greedy (p = 0.21). For algorithms requiring full solution construction, total computation time is reported; for methods returning instantaneous assignments, both time per decision and total time are shown.
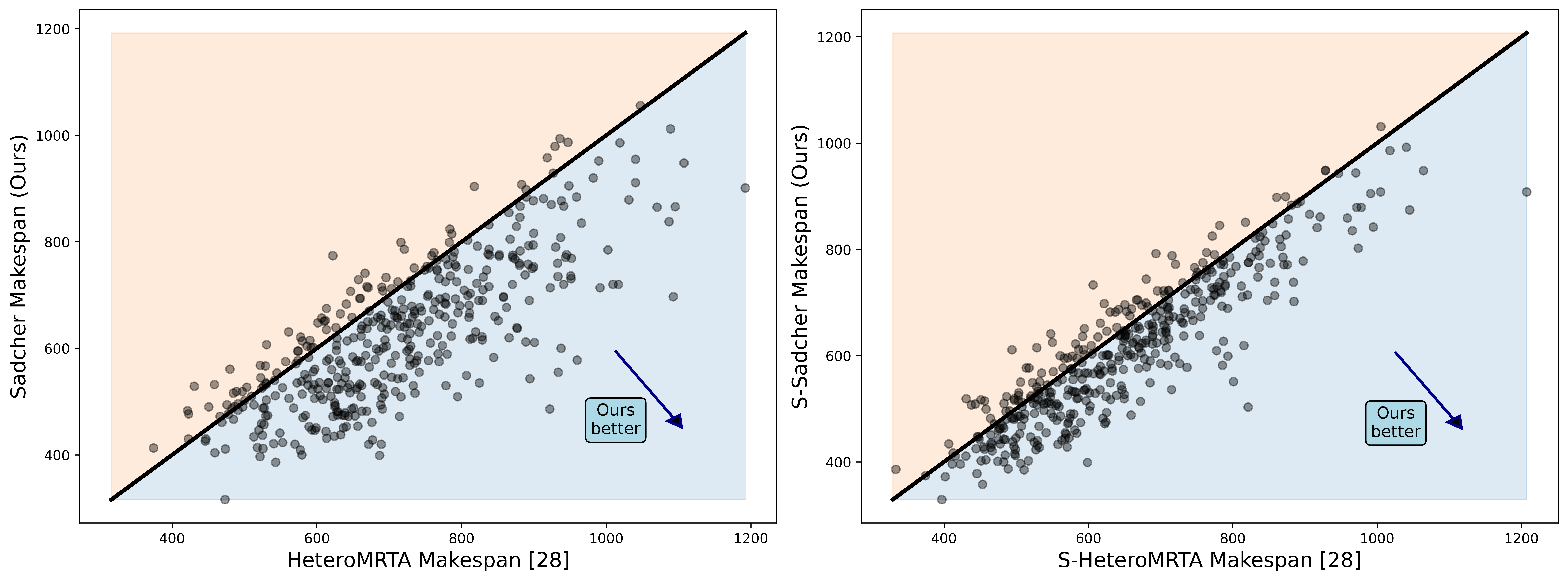
Pairwise makespan comparison of HeteroMRTA vs. Sadcher (left) and S-HeteroMRTA vs. S-Sadcher (right). Each point is one solved instance; points below the diagonal indicate better performance by (S-)Sadcher.
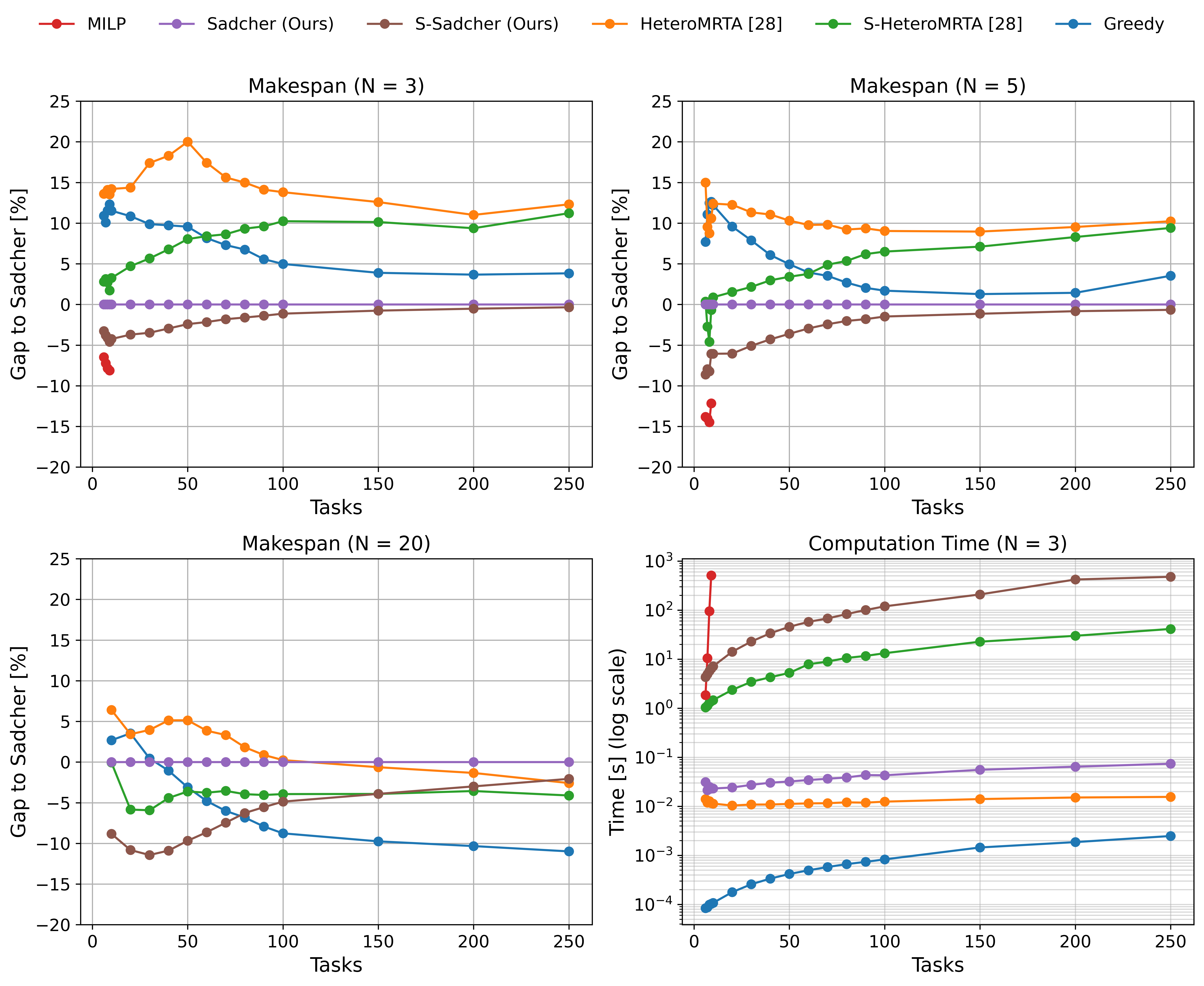
Relative makespan gap to Sadcher for 3, 5, and 20 robots (top left to bottom left). Bottom right: Computation time for 3 robots (for algorithms requiring full solution construction (Sample-HeteroMRTA, Sample-Sadcher, MILP), total computation time is reported, for methods returning instantaneous assignments (HeteroMRTA, Sadcher, Greedy), time per decision is reported). Task counts M ∈ [6, 250], with S = 3 skills and M/5 precedence constraints. Each point shows the mean over 100 runs.
Conclusion
In this work, we proposed Sadcher - an IL framework to address real-time task assignment for heterogeneous multi- robot teams, incorporating dynamic coalition formation and precedence constraints. The combination of reward predic- tion and relaxed bipartite matching yields strong performance with feasibility guarantees. Sadcher outperforms RL-based and heuristic baselines in makespan across small to medium- sized robot teams and a wide range of task counts. For bigger teams, the makespan advantage narrows. Sadcher can generate assignments in real-time across all tested problem sizes, but the sampling variant S-Sadcher is only real-time for smaller problems. Sadcher relies on a large (computationally expensive) dataset of expert demonstrations for training. Future work could extend our framework to incorporate battery budgets, deadlines, or time windows. Furthermore, fine-tuning IL policies with RL could increase performance on larger problem instances where expert solutions are very expensive or infeasible to obtain. Finally, the field would benefit from a standardized benchmark dataset. While our 250,000-instance dataset targets complex MRTA, expanding it with simpler, larger, and multi-objective scenarios would allow evaluation across a wider range of methods.Related Publications
Overcoming Explicit Environment Representations with Geometric Fabrics
In IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L),
2025.
Pushing Through Clutter With Movability Awareness of Blocking Obstacles
In IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA),
2025.
Scenario-based motion planning with bounded probability of collision
In The International Journal of Robotics Research (IJRR),
2025.
Globally-Guided Geometric Fabrics for Reactive Mobile Manipulation in Dynamic Environments
In IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L),
2025.
SHINE: Social Homology Identification for Navigation in Crowded Environments
In International Journal of Robotics Research (IJRR),
2025.
TamedPUMA: safe and stable imitation learning with geometric fabrics
In Learning for Dynamics and Control (L4DC),
2025.
Particle-based Instance-aware Semantic Occupancy Mapping in Dynamic Environments
In IEEE Transactions on Robotics (T-RO),
2025.
Topology-Driven Parallel Trajectory Optimization in Dynamic Environments
In IEEE Transaction on Robotics (T-RO),
2024.
Safe and stable motion primitives via imitation learning and geometric fabrics
In Robotics: Science and Systems, Workshop on Structural Priors as Inductive Biases for Learning Robot Dynamics,
2024.
Reactive grasp and motion planning for adaptive mobile manipulation among obstacles
In Robotics: Science and Systems, Workshop on Frontiers of Optimization for Robotics,
2024.
Evaluating Dynamic Environment Difficulty for Obstacle Avoidance Benchmarking
In IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS),
2024.
Physically Grounded Optimal Realizations of Symbolic Plans
In Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), Workshop on Frontiers of Optimization for Robotics,
2024.
Multi-Modal MPPI and Active Inference for Reactive Task and Motion Planning
In IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L),
2024.
Decentralized Multi-Agent Trajectory Planning in Dynamic Environments with Spatiotemporal Occupancy Grid Maps
In IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA),
2024.
Auto-Encoding Bayesian Inverse Games
In 16th Workshop on the Algorithmic Foundations of Robotics (WAFR),
2024.
Contingency Games for Multi-Agent Interaction
In Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L),
2024.
Learning to Play Trajectory Games Against Opponents with Unknown Objectives
In IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L),
2023.
RAST: Risk-Aware Spatio-Temporal Safety Corridors for MAV Navigation in Dynamic Uncertain Environments
In IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L),
2023.
Multi-Robot Local Motion Planning Using Dynamic Optimization Fabrics
In Proc. IEEE International Symposium on Multi-Robot and Multi-Agent Systems,
2023.